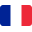
Regarding to the presence of mutations dogs are classified into three groups:
- Affected (mut/mut)- both alleles carry mutation, disease is clinically expressed
- Carrier (mut/wt)- one of two alleles carry mutation, disease is not clinically expressed
- Wild type (wt/wt)- mutation is not detected, normal genotype, healthy animal
For each group different breeding strategies can be applied in order to control the spread of the disease. Breeding with affected or carrier dogs should be avoided. In the case that the owner holds particularly valuable dog, which carry the mutation, such dog should be bred with healthy/unaffected individual. In the case where an affected dog was bred with healthy individual all animals of the offspring are carriers therefore genetic testing is not necessary (Figure 1). When first generation of dogs is bred again with healthy/unaffected animal 50% of the second generation of dogs is free of mutations (Figure 2). If two carrier animals are bred 25% of the offspring is healthy/unaffected (Figure 3). Second generation should be tested and only dogs which do not carry mutation are used for further breeding.
|
|
Affected |
||
|
Wild type |
Allele |
mut |
mut |
|
wt |
wt/mut (carrier) |
wt/mut (carrier) |
|
|
wt |
wt/mut (carrier) |
wt/mut (carrier) |
|
Figure 1
|
|
Carrier |
||
|
Wild type |
Allele |
wt |
mut |
|
wt |
wt/wt (wild type) |
wt/mut (carrier) |
|
|
wt |
wt/wt (wild type) |
wt/mut (carrier) |
|
Figure 2
|
|
Carrier |
||
|
Carrier |
Allele |
wt |
mut |
|
wt |
wt/wt (wild type) |
wt/mut (carrier) |
|
|
mut |
wt/mut (carrier) |
mut/mut (affected) |
|
Figure 3